UNIT ____: Prokaryotic Cells Name: _________________________
Essential Idea(s):
Prokaryotes have a much simpler cell structure than eukaryotes.
IB Assessment Statements and Class Objectives | |
1.2.U1 | Prokaryotes have a simple cell structure without compartmentalization.
|
1.2.S1
| Drawings of the ultrastructure of prokaryotic cells based on electron micrograph.
|
3.2.U1 | Prokaryotes have one chromosome consisting of a circular DNA molecule.
|
3.2.U2 | Some prokaryotes also have plasmids but eukaryotes do not.
|
1.2.U3 | Prokaryotes divide by binary fission.
|
6.3.U7 | Antibiotic blocks processes that occur in prokaryotic cells but not in eukaryotic cells.
|
6.3.A3 | Florey and Chain’s experiments to test penicillin on bacterial infections in mice.
|
6.3.NOS | Risks associated with scientific research- Florey and Chain’s tests on the safety of penicillin would not be compliant with current protocol on testing.
|
6.3.U8 | Viruses lack a metabolism and cannot therefore be treated with antibiotics.
|
1.2.U1
Prokaryotes have a simple cell structure without compartmentalization
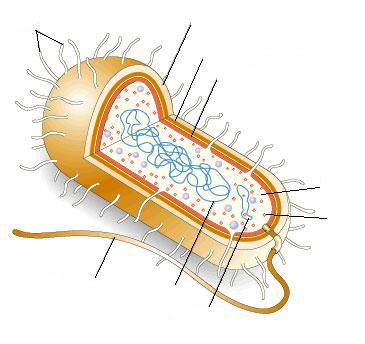
List the functions of the following structures of a prokaryotic cell:
Define “extracellular.”
Highlight the extracellular structures of a prokaryotic cell.
1.2.S1
Drawings of the ultrastructure of prokaryotic cells based on electron micrographs
Explain why the ultrastructure of prokaryotic cells must be based on electron micrographs.
Draw the ultrastructure of E. coli based on an electron micrograph.
The line segment corresponds to 0.5 μm
3.2.U1 / 3.2.U2
Prokaryotes have one chromosome consisting of a circular DNA molecule
Some prokaryotes have plasmids but eukaryotes do not
Nucleoid Describe the structure and function of nucleoid DNA | Plasmid Describe the structure and function of plasmid DNA |
Define “naked” in relation to prokaryotic DNA:
Compare the genetic material of prokaryotes and eukaryotes:
PROKARYOTIC DNA | EUKARYOTIC DNA |
1.2.U3
Prokaryotes divide by binary fission
Define asexual reproduction and binary fission.
Outline the steps of binary fission.
Prokaryote Metabolism
6.3.A3
Florey and Chain’s experiments to test penicillin on bacterial infections in mice.
Florey and Chain were the scientists who followed up most successfully on Alexander Fleming’s discovery of penicillin. Annotate the diagram of one of their experiments to test the effect of penicillin on treating a bacterial infection.
6.3.NOS
Risks associated with scientific research- Florey and Chain’s tests on the safety of penicillin would not be compliant with current protocol on testing
Florey followed up the mice experiments with additional testing on more mice and in sick humans.
Summarize the first human test of antibiotics:
Compare allowable research risks of the past with those of the present.
Past | Present |
6.3.U8
Viruses lack a metabolism and cannot therefore be treated with antibiotics.
Explain why antibiotics are ineffective against viruses:
6.3.U7
Antibiotics block processes that occur in prokaryotic cells but not in eukaryotic cells
Define antibiotic:
Outline the mechanism by which antibiotics kill bacteria:
Read the information at the following two websites and annotate the notes with 1) the name of one example antibiotic for each type of antibiotic action and 2) a brief summary of why each antibiotic class effects prokaryotic cells but not eukaryotic cells.