UNIT _____: Aerobic Respiration Name: _____________________
Essential Idea(s):
Energy is converted to a usable form in cell respiration
IB Assessment Statements and Class Objectives |
2.8.U4: Aerobic cell respiration requires oxygen and gives a large yield of ATP from glucose
- Compare the total amount of ATP made from anaerobic and aerobic respiration.
- State the location of aerobic respiration.
2.8.S1: Analysis of results from experiments involving measurement of respiration rates in germinating seeds or invertebrates using a respirometer
- Outline the use of a respirometer to measure cellular respiration rate.
2.8.NOS: Assessing the ethics of scientific research- the use of invertebrates in respirometers experiments
- List ethical questions that must be considered before using animals in experiments.
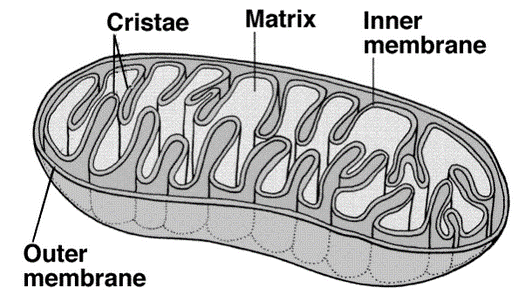
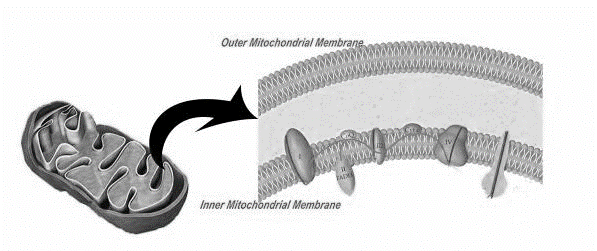
8.2.U12: The structure of the mitochondrion is adapted to the function it performs
- Outline how mitochondria structure could evolve through natural selection.
- State evidence that suggests mitochondria were once free living prokaryotes.
8.2.S2: Annotations of a diagram of mitochondrion to indicate the adaptations to its function
- Draw and label a diagram of the mitochondria.
- State the function of the following mitochondrial structures: outer membrane, inner membrane, cristae, intermembrane space, matrix, ribosome and mtDNA..
8.2.A1: Electron tomography used to produce images of active mitochondria
- State that electron tomography enables scientists to view the dynamic nature of mitochondrial membranes.
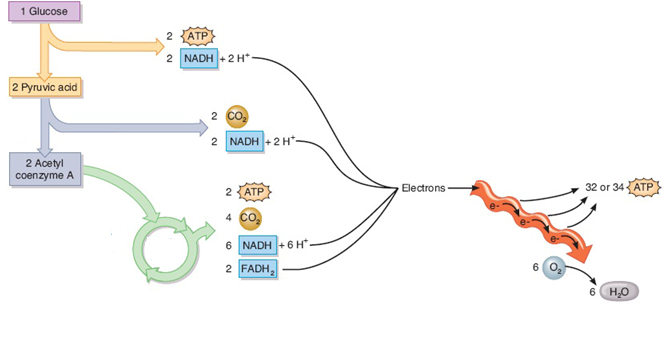
8.2.U5: In aerobic cell respiration pyruvate is decarboxylated and oxidized
- Define decarboxylation and oxidation.
8.2.U6: In the link reaction pyruvate is converted into acetyl coenzyme A.
- Summarize the reactant and products of the link reaction.
8.2.U7: In the Krebs cycle, the oxidation of acetyl groups is coupled to the reduction of electron carriers, liberating carbon dioxide
- State that NADH and FADH2 are electron carriers formed during the Krebs cycle.
- Outline the events of the Krebs cycle, referencing the formation of NADH and FADH2, formation of ATP and decarboxylation of acetyl groups.
8.2.S1: Analysis of diagrams of the pathways of aerobic respiration to decide where decarboxylation and oxidation reactions occur.
- State that decarboxylation of glucose occurs in the linking reaction and Krebs cycle of aerobic respiration.
8.2.U8: Energy released by oxidation reactions is carried to the cristae of the mitochondria by reduced NAD and FAD
- State that NAD+ is reduced to become NADH in the link reaction and Krebs cycle.
- State that FAD is reduced to become FADH2 in the Krebs cycle.
- State that NADH and FADH2 carry electrons to the electron transport chain on the mitochondrial inner membrane.
8.2.U9: Transfer of the electrons between carriers in the electron transport chain in the membrane of the cristae is coupled to proton pumping.
- State that at the electron transport chain, FADH2 and NADH given electrons to electron carrier proteins.
- State that the movement of electrons through electron carrier proteins in the electron transport chain is used to pump protons (H+) across the inner mitochondrial membrane into the intermembrane space.
8.2.U11: Oxygen is needed to bind with the free protons to maintain the hydrogen gradient, resulting in the formation of water
- State that oxygen is the final electron acceptor in aerobic cellular respiration.
- State that that formation of water in the matrix at the end of the electron transport chain helps to maintain the hydrogen gradient between the intermembrane space and the matrix.
8.2.U10: In chemiosmosis protons diffuse through ATP synthase to generate ATP.
- Define oxidative phosphorylation and chemiosmosis.
8.2.NOS: Paradigm shift-chemiosmotic theory led to a paradigm shift in the field of bioenergetics.
- State that Peter Mitchell’s proposal of the chemiosmotic hypothesis in 1961 lead to a major shift in our understanding of cellular processes.

Cellular Respiration:
Definition:
Formula:
Overview:
Respirometers – a tool used to measure respiration rates
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=RRRzC1yohHY
A sealed container for…
| An alkali, such as potassium hydroxide, to… | A capillary tube with fluid for… |
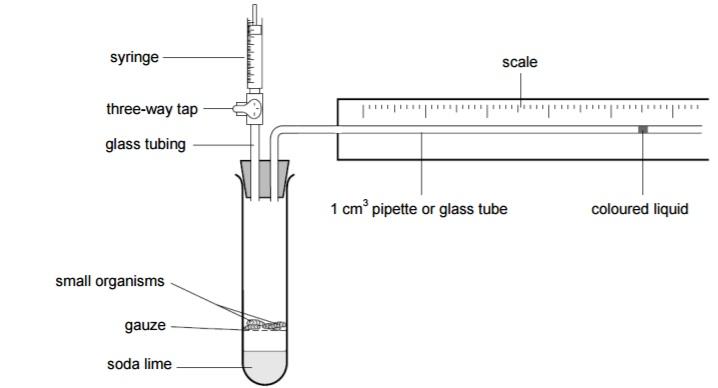
What Happens:
- Organism performs cellular respiration
- CO2 produced is absorbed by the alkali (so we know change in gas volume and pressure is due to reduction in O2, not increase of CO2 during respiration).
- There is a reduction in O2 gas as it is used up during respiration, reducing the volume of air in the respirometer
- Pressure drops in the container as there is less gas
- The drop in pressure in the container causes the movement of the fluid in the capillary tube
Variable to Control and/or Manipulate:
- Temperature
- Amount of living material
- Type of organism
Responding Variable:
Ethics of Animal Use:
Mitochondria Structure and Function
Review: Glycolysis
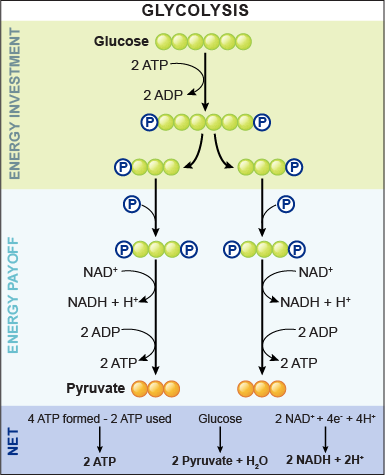
Review of Glycolysis
- Occurs __________________ OR ___________________
- Occurs in the _________________
- Glucose 🡪 2 ______________
- Produces a net of ______________ and _________________
The Linking Reaction
- Only when oxygen is ________________
- Pyruvate (from glycolysis) enters the __________________ of the mitochondria
- A single ______________ is removed (leaves as ________) creating a molecule called ___________.
The removal of a carbon is called “DECARBOXYLATION”
- The ___________________ out of the mitochondria and through the cell membrane
- The oxidation of pyruvate is coupled to the reduction of NAD+, creating _____________________
- A large molecule called ____________________________ joins with the acetyl. Creates _________________________________________________
- Each linking reaction creates:
- __________________
- __________________
Remember: 1 glucose produces 2 pyruvate, so the linking reaction happens two times per glucose
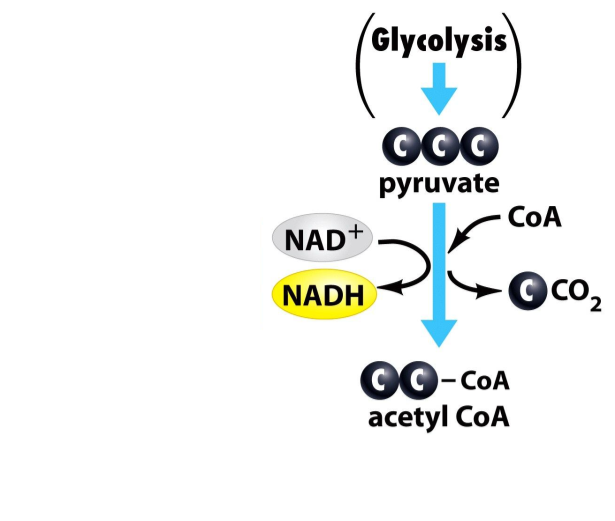
The Krebs Cycle
- Only when oxygen is ________________
- Occurs in the mitochondrial ________________
- The cycle is 8 steps, each enzyme mediated. Releasing the energy in steps prevents much of the energy from ________________________________________________
- Four major steps:
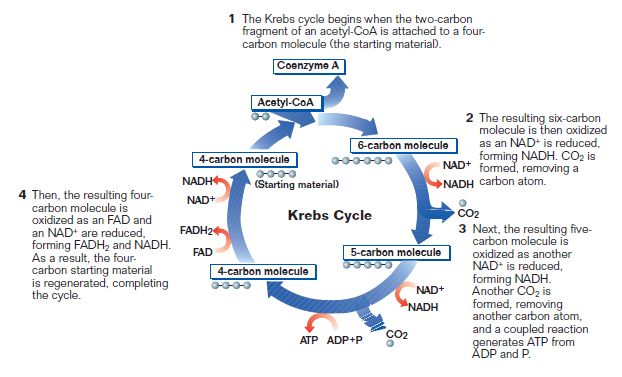
- _________________
- _________________ (will be used later in the ETC)
- _________________ (will be used later in the ETC)
- _________________ (via substrate level phosphorylation, can be used to do cell work)
Remember: 1 glucose produces 2 pyruvate, so the cycle happens 2X per glucose
After the Krebs Cycle, the carbons from our original glucose molecule are GONE…




What remains are the electrons that have been given to the electron carrier molecules NADH and FADH2… these molecules move on to the Electron transport chain (ETC).
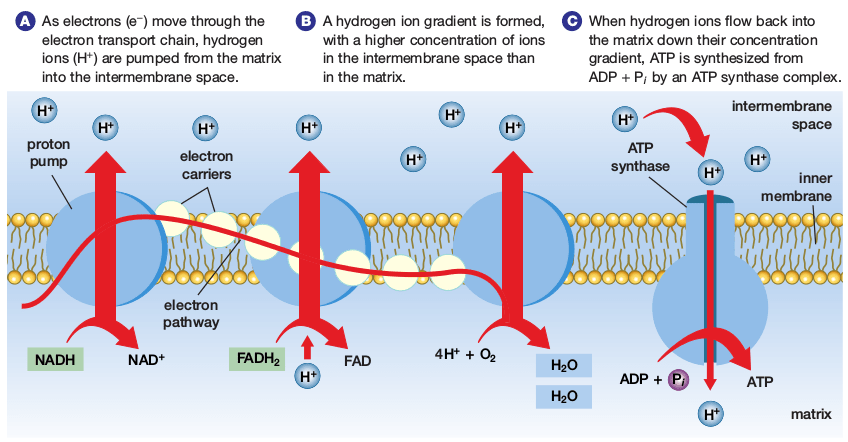
- A chain of proteins located on the inner mitochondrial membrane
- The inner membrane has many infoldings, called __________________
- The cristea increase the __________________of the membrane, allowing for many ETCs
- __________________________________ (created in glycolysis, the linking reaction and the Krebs cycle) give up their __________________ to the electron carrier proteins of the ETC.
- The NADH and FADH2 are __________________ and the electron carriers are ______________
- The __________________pass from protein to protein, __________________ is released at each step
- The energy is used to pump ___________ out of the inner compartment.
- This creates a ________________________
- ________________________ accumulate in ____________________________________
- At the end of the chain, the “spent” electrons joins with __________________ and H+ to yield water. THIS IS WHY OXYGEN IS NEEDED IN AEROBIC RESPIRATION!
Chemiosmosis
- The _________________________ passively move back through mitochondrial membranes through __________________ (an enzyme embedded in the inner membrane)
- The movement of protons (H+) is coupled to the phosphorylation of ADP to yield ATP
- Yields __________________ ATP per glucose
Together, the electron transport chain and chemiosmosis are called OXIDATIVE PHOSPHORYLATION, because ADP is phosphorylated to produce ATP, using energy release by oxidation of the electron carrier molecules.
Summary