UNIT ____: Fermentation Name: _________________________
Essential Idea(s):
Cell respiration supplies energy for the functions of life
IB Assessment Statements and Class Objectives |
2.8.U1: Cell respiration is the controlled release of energy from organic compounds to produce ATP
- Define “cell respiration.”
- State the reaction for cellular respiration.
- State the types of organic compounds used in cellular respiration by animals and plants.
2.8.U2: ATP from cell respiration is immediately available as a source of energy in the cell
- State three example uses of cellular energy.
- Outline energy transfer in the formation and use of ATP.
- State three reasons why cellular respiration must be continuously performed by all cells.
8.2.U3: In glycolysis, glucose is converted to pyruvate in the cytoplasm
- Outline the glycolysis reaction, including phosphorylation, lysis and energy harvest.
8.2.U2: Phosphorylation of molecules makes them less stable.
- Define phosphorylation.
- State the consequence of a molecule being phosphorylated.
8.2.U4: Glycolysis gives a small net gain of ATP without the use of oxygen
- State the formula for the glycolysis reaction.
- State that glycolysis occurs in both anaerobic and aerobic respiration.
- State that glycolysis is an example of a metabolic pathway.
8.2.U1: Cell respiration involves the oxidation and reduction of electron carriers
- Outline oxidation and reduction reactions in terms of movement of electrons, hydrogen or oxygen atoms.
- Define “electron carrier.”
- State the name of the electron carrier molecule used in cellular respiration.
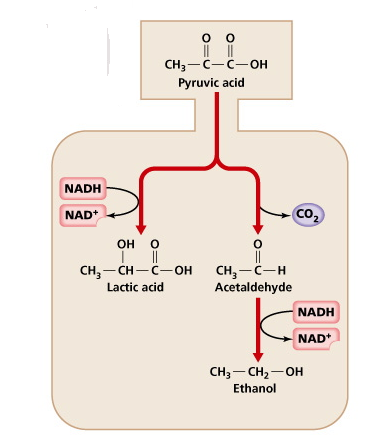
2.8.U3: Anaerobic cell respiration gives a small yield of ATP from glucose
- Define “anaerobic respiration”
- List three situations in which anaerobic respiration is useful.
- Compare anaerobic respiration in yeasts and humans.
2.8.A1: Use of anaerobic cell respiration in yeasts to produce ethanol and carbon dioxide in baking.
- Outline how anaerobic respiration in yeast is used in baking.
- Outline how anaerobic respiration in yeast is used in ethanol production.
2.8.A2: Lactate production in humans when anaerobic respiration is used to maximize the power of muscle contractions
- State the condition in which humans would perform anaerobic respiration.
- Outline production of lactate in humans during anaerobic respiration.
What is Cellular Respiration?

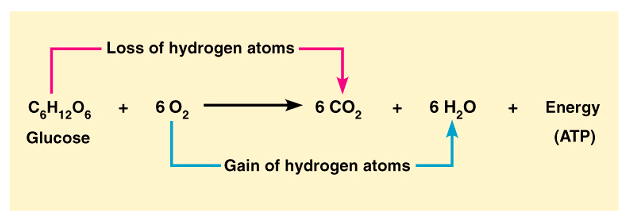
Cellular respiration is a Redox Reaction!
Glucose 🡪 carbon dioxide = ___________
Oxygen gas 🡪 water = ______________



Cellular Respiration is a Combustion Reaction
- Oxidizing glucose in cells is same overall reaction as burning it in a fire.
- In fire, the energy is lost as heat in a ______________________
- In cells, a _________________________ occur to reduce energy lost as heat and to capture the energy in chemical bonds.
Adenosine-5'-triphosphate (ATP) is the prime energy carrier for all cells:
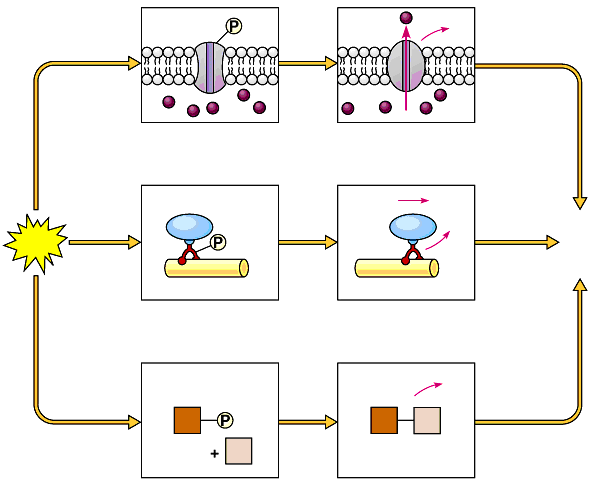
How ATP does work: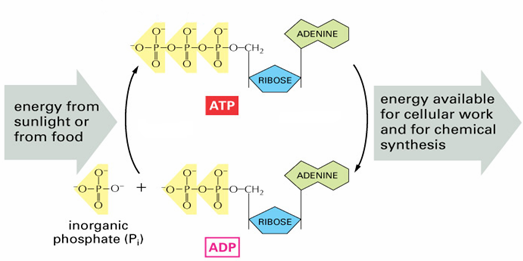
- A kinase enzyme transfers a phosphate group from ATP to another molecule (a “substrate”). The process is referred to as phosphorylation.
- The phosphorylated substrate molecule is now “activated!” When the substrate loses its Pi, it can use the energy released to do cellular work.
- The Pi can be “recycled” and added to an ADP to create a new ATP 🡪 this is what cellular respiration is all about!!!
Overview of Cellular Respiration
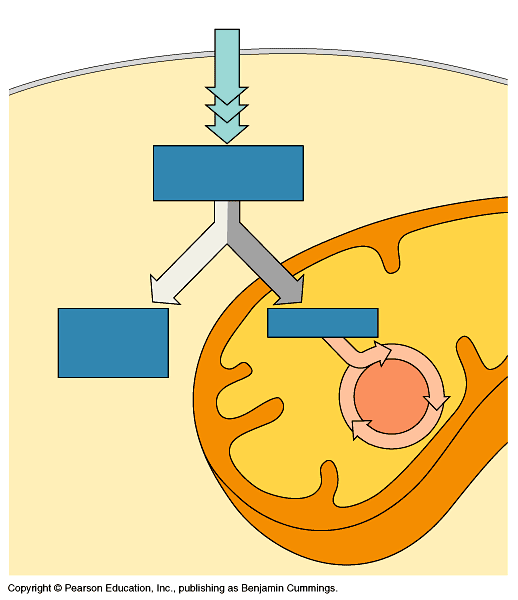




Glycolysis
An example of a metabolic pathway


The models show the number of carbons in each molecule, not the structural formula.
Energy investment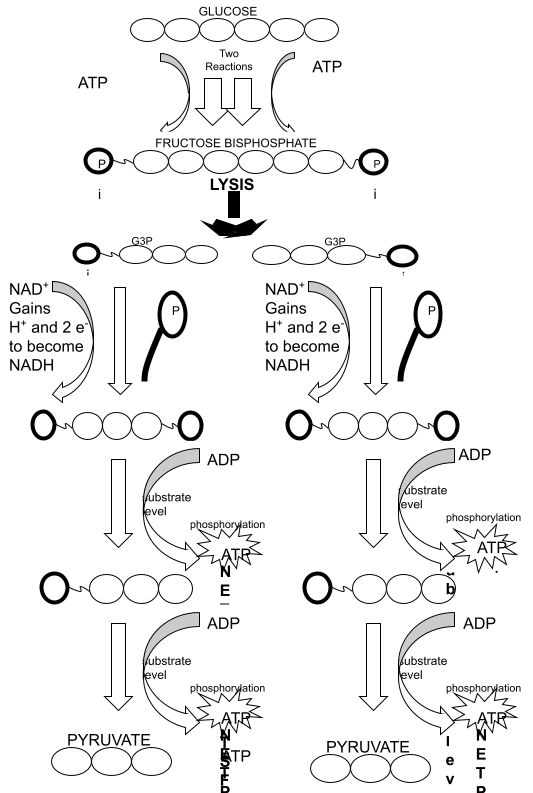
Lysis
Energy
harvesting
phase

Electron Carrier Molecules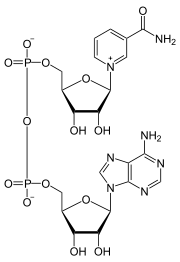
- Electron carriers are molecules that can accept and give up electrons.
- The main electron carrier in cellular respiration is NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide)
NAD+ ___________________________ from other molecules
to form _________
Anaerobic Respiration
Definition:
Useful when: