UNIT ____: Transcription Name: __________________
Essential Idea(s):
Information stored as a code in DNA is copied onto mRNA.
2.7.U4: Transcription is the synthesis of mRNA copied from the DNA base sequences by RNA polymerase
- Define transcription.
- Outline the process of transcription, including the role of RNA polymerase and complementary base pairing.
- Identify the sense and antisense strands of DNA given a diagram of translation.
7.2.A1: The promoter as an example of non-coding DNA with a function
- Outline the role of promoter DNA.
7.2.U4: Transcription occurs in a 5’ to 3’ direction
- Describe the initiation of transcription, including the role of the promoter, transcription factors, the TATA box and RNA polymerase.
- Describe elongation of transcription, including the role of nucleotide triphosphates and the direction of transcription.
- Describe termination of transcription, including the role of the terminator.
7.2.U5: Eukaryotic cells modify mRNA after transcription
- List two major differences in gene expression between prokaryotic cells and eukaryotic cells.
- Describe the three post-transcriptional modifications of pre-mRNA in eukaryotes.
7.2.U6: Splicing of mRNA increases the number of different proteins an organism can produce.
- Describe the process of alternative RNA splicing.
- Outline an example of alternative splicing the results in different protein products.
From Gene to Protein: An Overview
- A genome is _______________________________________________________________.
- The human genome is __________________base pairs long, spread among ____ chromosomes.

- Genomes have DNA sequences that occur with different frequencies.
- Some DNA sequences only occur __________ in the entire genome
- Most genes are ____________, single copy DNA sequences
- A gene is: _____________________________________________
- Only about ______ of the human genome is genes
- Human DNA contains about ___________________ protein coding genes
- Some DNA sequences are _____________________________________ in the genome
- These are called ______________________________________ sequences
- 98% of the DNA consists of __________________________________, which may:
- Although genes get a lot of attention, it’s the ________________ that perform most life functions and even make up the majority of cellular structures.
- Proteins are large, complex molecules made up of smaller subunits called _______________.
- Functions of proteins include:
- __________________________
- __________________________
- __________________________
- __________________________
- __________________________
- __________________________
- __________________________
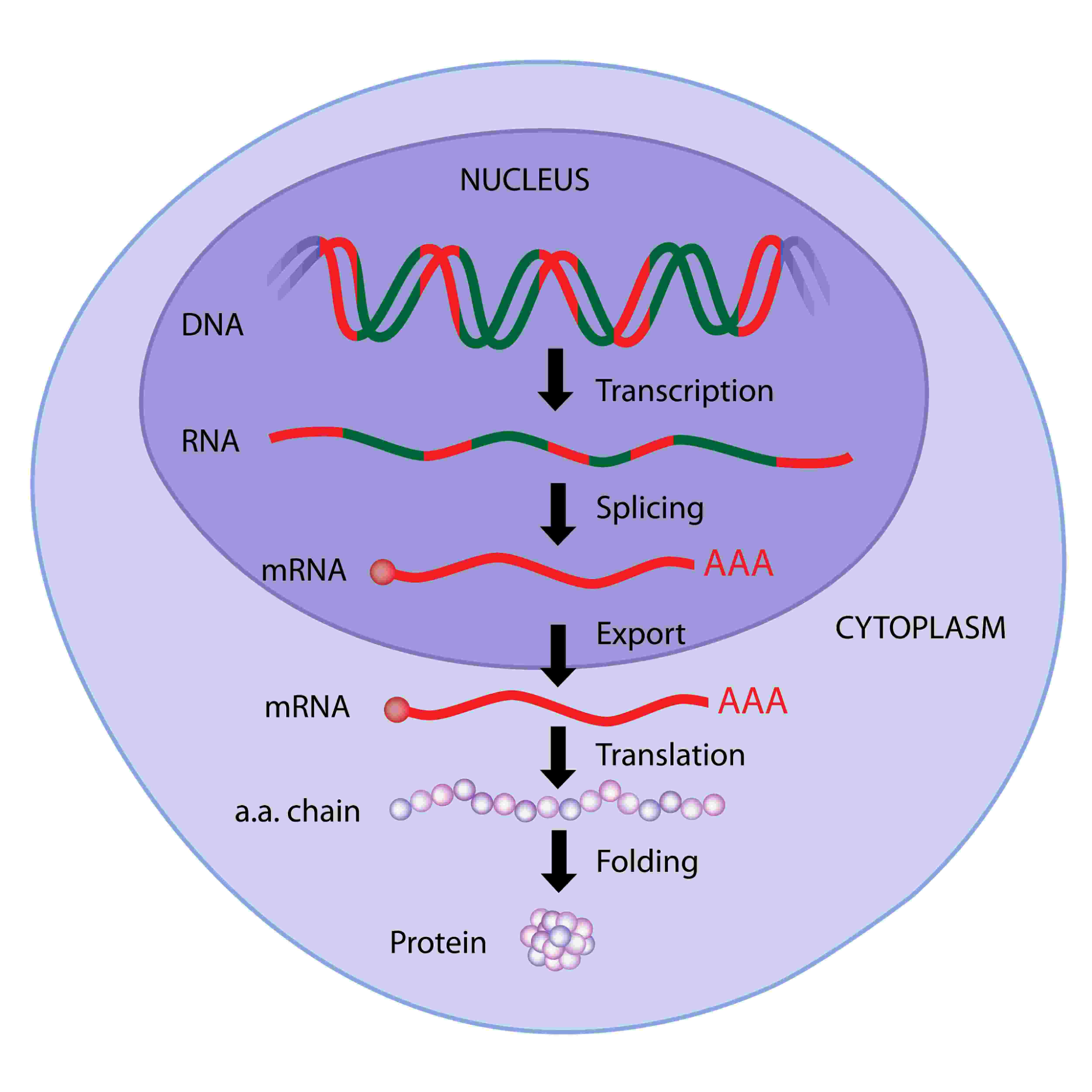
The path from gene to protein has three steps:
- In _________________, molecules of RNA are produced from the DNA in the nucleus.
- During ______________________, the RNA is modified before leaving the nucleus and non-protein coding regions of the RNA strand are removed.
- In ___________, RNA molecules are used as a code for protein assembly at the ribosome.
TRANSCRIPTION NOTES |
What: |
|
Where: | Prokaryotes: Eukaryotes: |
Why: | DNA is too fragile and important for the cell to risk having it leave the safety of the nucleus. The cytoplasm is a scary place for DNA (there are enzymes there that break DNA apart) so the cells send RNA into the cytoplasm as a copy of the genetic information, leaving the original information safe in the nucleus.
|
How:
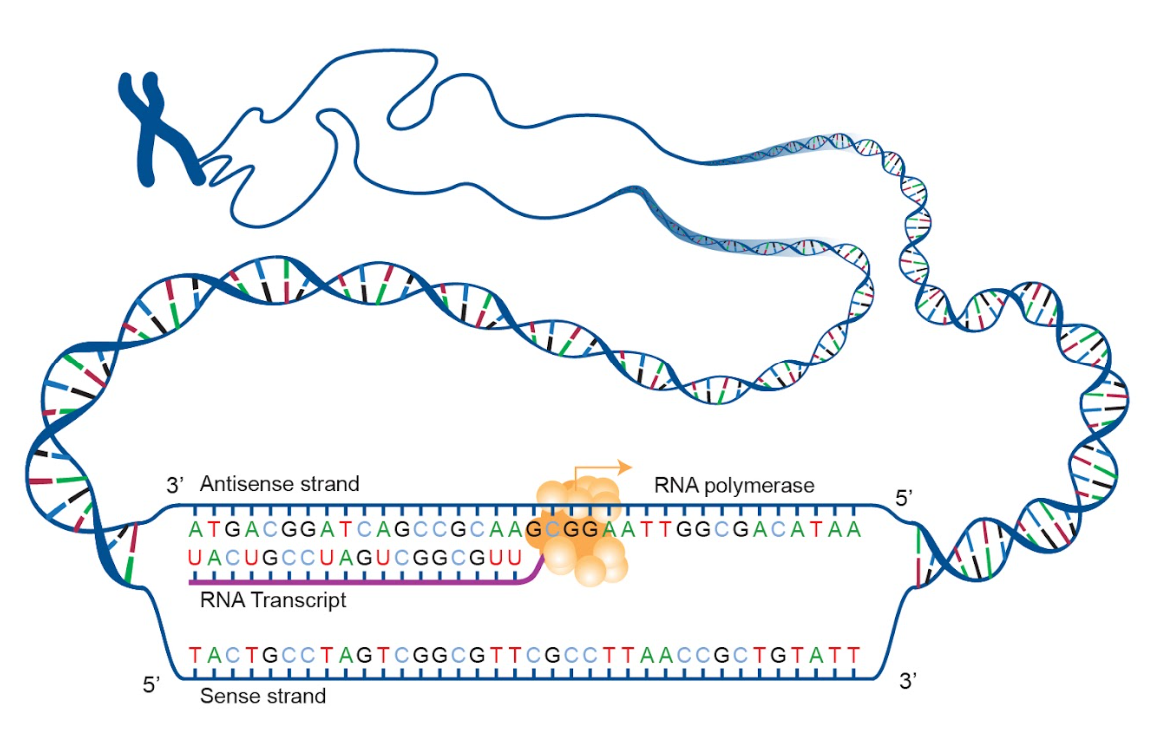
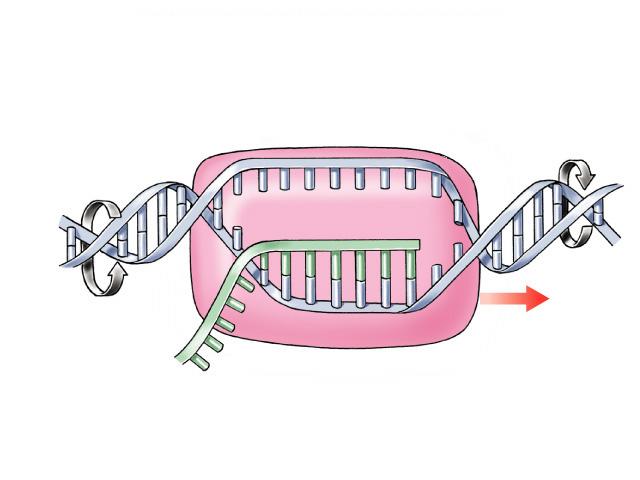
| Note: before transcription begins in eukaryotes, the DNA has to uncoil from the nucleosome. If the DNA is not uncoiled from the histone proteins, the enzyme required for transcription cannot get close enough to the DNA to attach. This is one way eukaryotic cells are able to regulate whether a gene is transcribed. In other words, by remaining coiled in a nucleosome the gene is turned “off.” When the DNA uncoils, the gene can be turned “on.” Remember, prokaryotes have naked DNA (no histones), so they are unable to control genes in this way. Initiation (describe the initiation phase of transcription using and defining the terms promoter, TATAA box, transcription factors, and RNA polymerase II)

Elongation (describe the elongation phase of transcription using the terms RNA polymerase II, RNA nucleotides, uracil, complementary, 5’ 🡪 3’, nucleotide triphosphates and template). NOTE: In double-stranded DNA, only one strand codes for the RNA that is translated into protein. This DNA strand is referred to as the antisense strand. The strand that does not code for RNA is called the sense strand. Although these strands are exact mirror images of one another, only the antisense strand contains the information for making proteins. The sense strand does not.
|
| Termination (describe the termination phase of transcription using and defining the term terminator)

|
RNA VS DNA
| DNA | RNA |
Type of Sugar |
|
|
Number of Strands |
|
|
Structure of Sugar (drawn) |
|
|
Name of Bases |
|
|
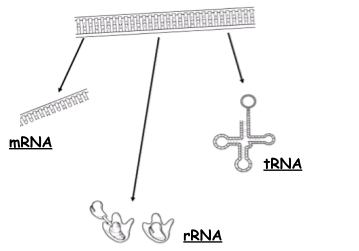
(Some of the) Types of RNA

RNA Modification


RNA Processing http://vcell.ndsu.nodak.edu/animations/mrnaprocessing/advanced.htm |
What: | Most newly transcribed pre-mRNA molecules undergo various alterations to yield the mature product, mRNA. This happens in eukaryotes ONLY. RNA processing does NOT happen in prokaryotic cells. |
Where: | Nucleus |
How:
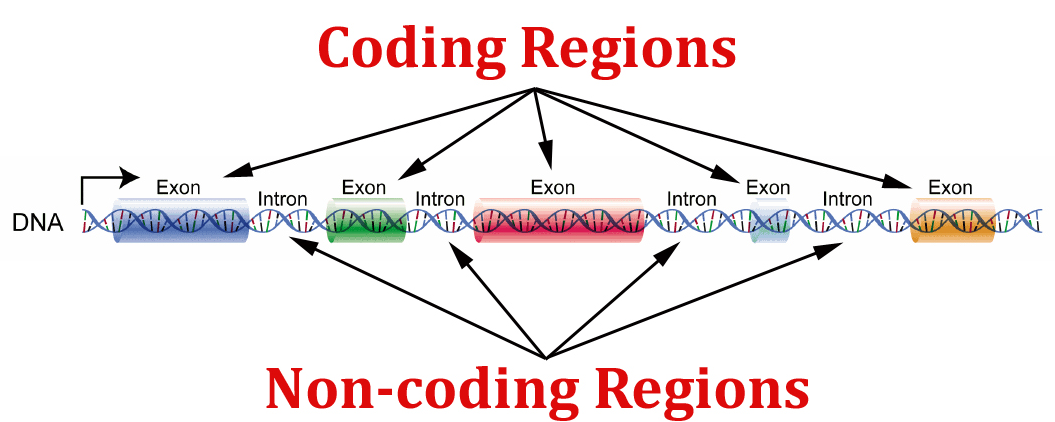
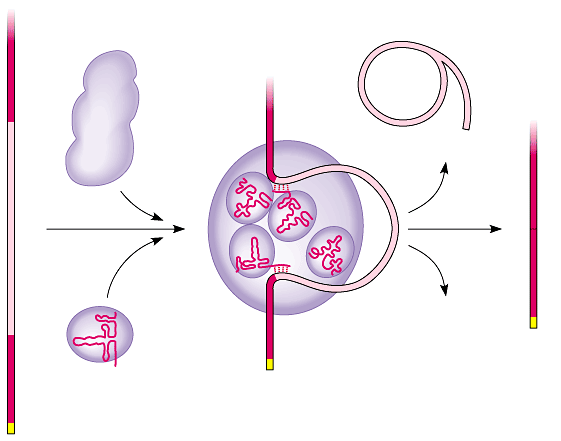
| During ______________, non-protein coding regions of the RNA strand are removed - Eukaryotic genomes contain a large amount of DNA that does not code for proteins.
- EXONS:
- INTRONS:
- The ____________ are “_____________” out of the RNA and the ___________ are joined together
- Done by RNA splicing enzymes
- snRNPs
- Spliceosome
- In contrast to prokaryotes, eukaryotic genomes contain a large amount of ___________. An increase in complexity is associated with an increase in the proportion of non-protein-coding DNA.
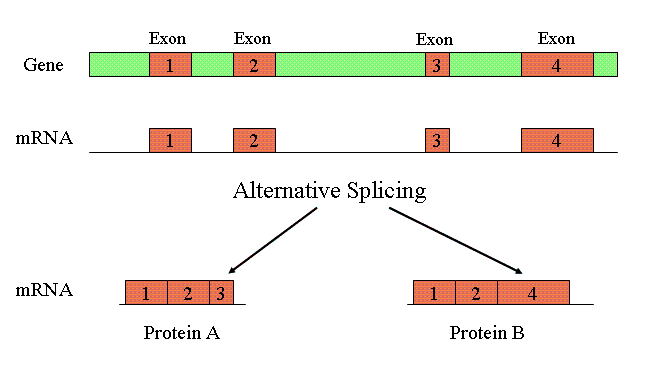
- Alternative Splicing: One gene can encode for a series of related proteins which are derived from the same gene by alternative splicing pathways
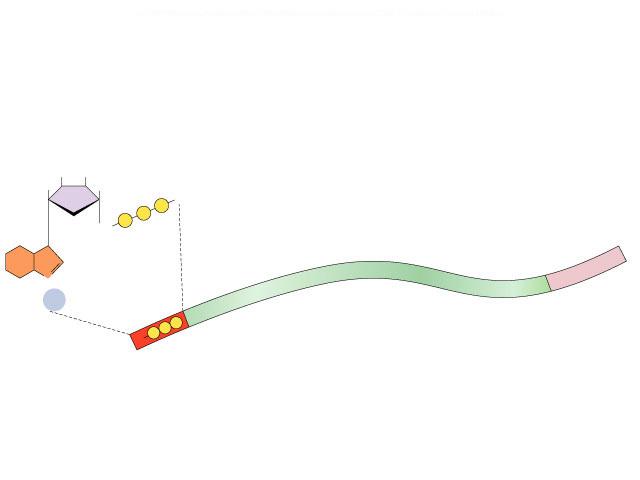
- During _____________________, the RNA is modified before leaving the nucleus.
- Need to protect mRNA from enzymes in cytoplasm that ______________________
- Protect the ends of the molecule by adding a
- __________________
- __________________ (longer tail, mRNA lasts longer: produces more protein)
|
