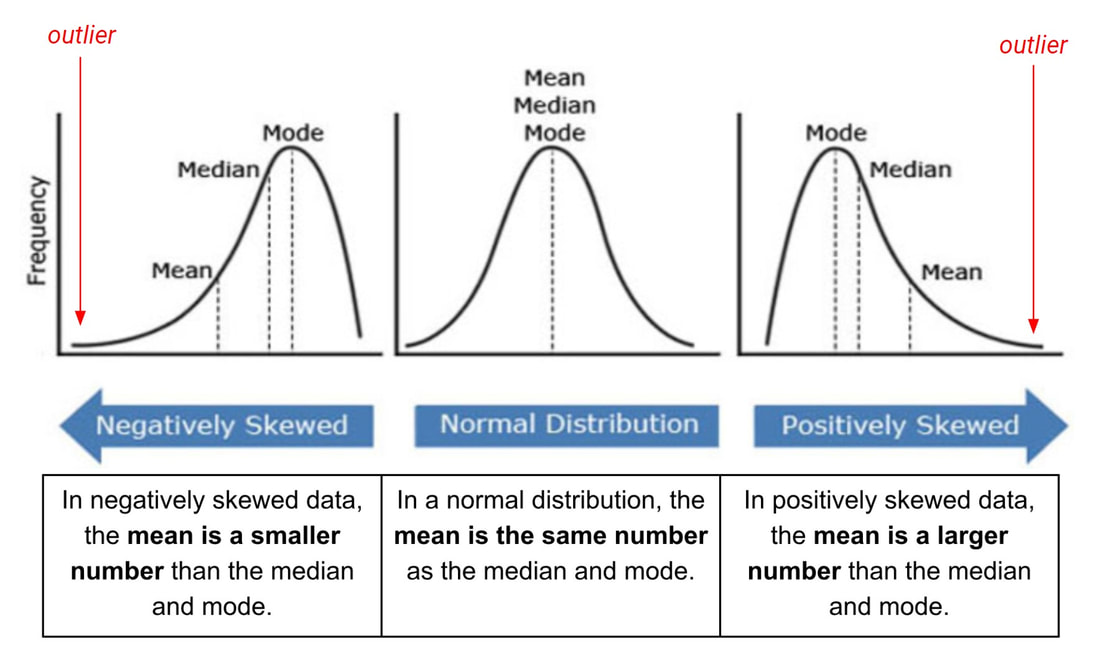
An outlier is an observation that lies an abnormal distance from other values in a random sample from a population.
Outliers can cause a data set to be “skewed” from a normal bell curve distribution. By doing so, outliers can have a disproportionate effect on statistical results, such as the mean, which can result in misleading interpretations.
A data point is categorized as an outlier if it is more than 1.5 × IQR (interquartile range) above the third quartile or below the first quartile.
There are online calculators to determine if a data set contains an outlier. Use your search engine to look up “outlier IQR calculator”