UNIT ____: Meiosis Name: _____________________
Essential Idea(s):
- Alleles segregate during meiosis allowing new combinations to be formed by the fusion of gametes.
- Meiosis leads to independent assortment of chromosomes and unique composition of alleles in daughter cells.
IB Assessment Statements and Class Objectives
3.3.NOS: Making careful observations- meiosis was discovered by microscope examination of dividing germ-line cells.
- Discuss difficulties in microscopic examination of dividing cells.
- Describe the discovery of meiosis.
3.3.U2: The halving of the chromosomes number allows a sexual life cycle with fusion of gametes.
- Compare sexual and asexual life cycles.
- Explain why meiosis must occur as part of a sexual life cycle.
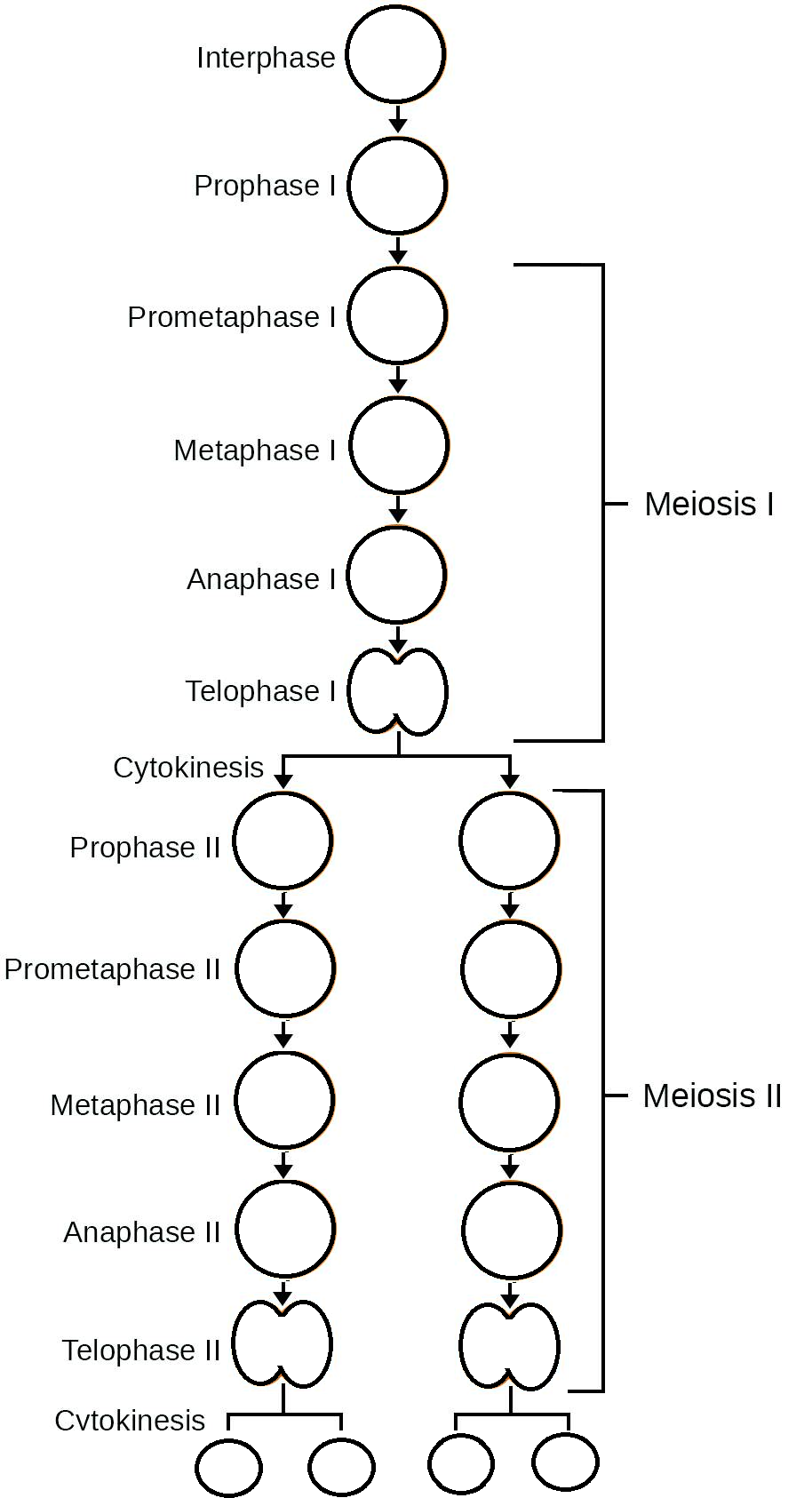
3.3.U1: One of diploid nucleus divides by meiosis to produce four haploid nuclei .
- Compare divisions of meiosis I and meiosis II.
3.3.S1: Drawing diagrams to show the stages of meiosis resulting in the formation of four haploid cells.
- Outline the events of prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase in meiosis I and meiosis II.
- Draw diagrams of cells in prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase in meiosis I and meiosis II.
3.3.U3: DNA is replicated before meiosis so that all chromosomes consist of two sister.
- State that DNA is replicated in interphase before meiosis.
- Given a diploid number (for example 2n=4), outline the movement and structure of DNA through the stages of meiosis.
10.1.U1: Chromosomes replicate in interphase before meiosis.
- Identify tetrad, bivalent, sister chromatids and non-sister chromatids in diagrams of replicated chromosomes.
3.3.U4: The early stages of meiosis involved pairing of homologous chromosomes and crossing over followed by condensation.
- List three events that occur in prophase 1 of meiosis.
- Define bivalent and synapsis.
- Outline the process and result of crossing over.
10.1.U2: Crossing over is the exchange of DNA material between non-sister homologous chromatids.
- State that crossing over occurs during prophase I.
- Define chiasmata.
10.1.U3: Chiasmata formation between non-sister chromatids can results in an exchange of alleles.
- State two consequences of chiasmata formation between non-sister chromatids.
10.1.S1: Drawing diagrams to show chiasmata formed by crossing over.
- Draw a diagram to illustrate the process and result of crossing over.
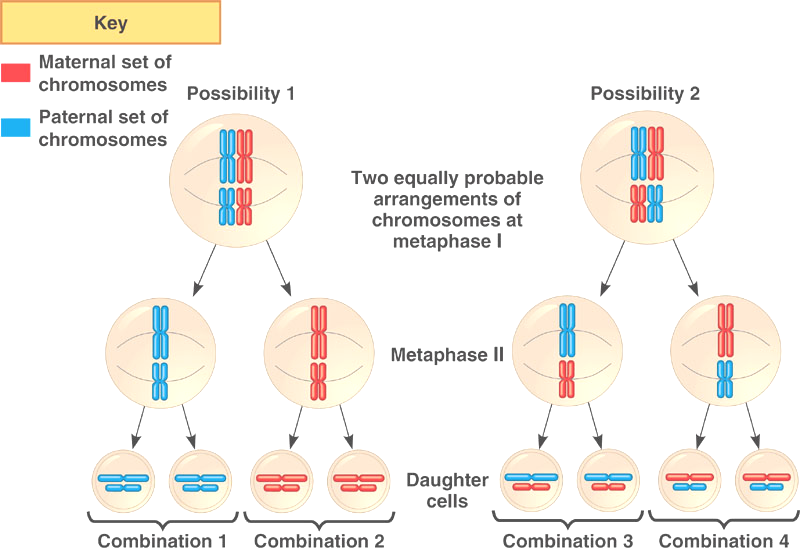
3.3.U5: Orientation of pairs of homologous chromosomes prior to separation is random.
- Describe the attachment of spindle microtubules to chromosomes during meiosis I.
- Describe random orientation of chromosomes during meiosis I.
10.1.U6: Independent assortment of genes is due to the random orientation of pairs of homologous chromosomes in meiosis 1.
- Describe random orientation and independent assortment.
- Given a parent cell genotype, determine the allele combinations that are possible in the gametes due to independent assortment and random orientation.
10.1.U5: Homologous chromosomes separate in meiosis I .
- Contrast meiosis I with meiosis II.
3.3.U6: Separation of pairs of homologous chromosomes in the first division of meiosis halves the chromosome number.
- Explain why meiosis I is a reductive division.
- State that cells are haploid at the end of meiosis I.
10.1.U7: Sister chromatids separate in meiosis II.
- Compare meiosis II with mitosis.
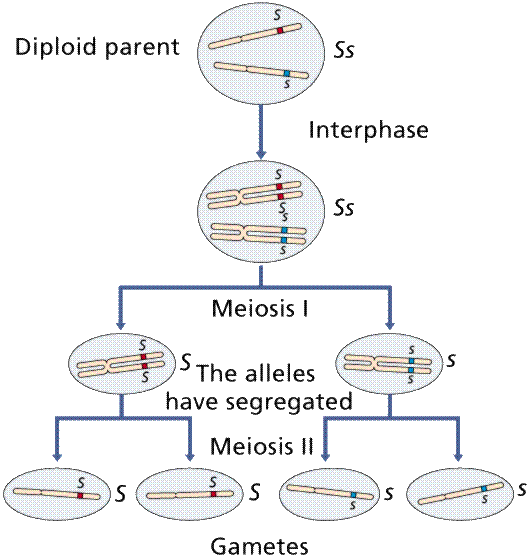
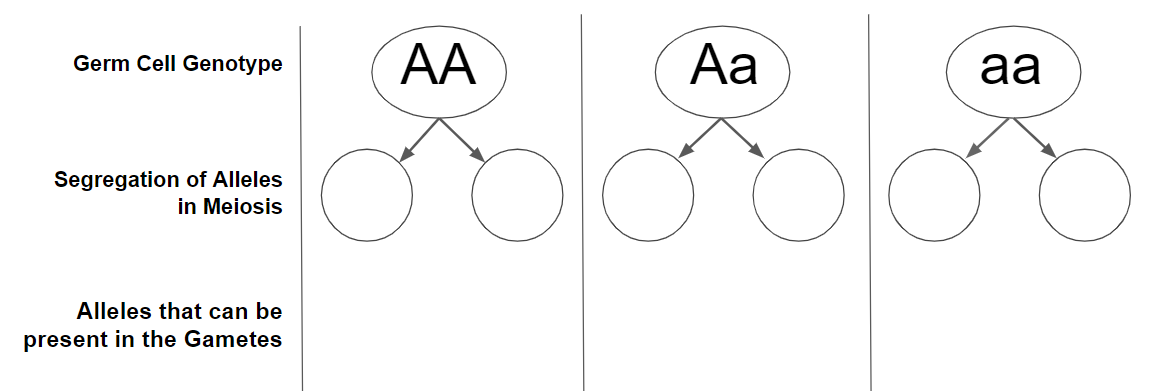
3.4.U3: The alleles of each gene separates into different haploid daughter nuclei during meiosis.
- State the outcome of allele segregation during meiosis.
10.2.U1: Unlinked genes segregate independently as a result of meiosis.
- State the difference between independent assortment of genes and segregation of alleles.
- Describe segregation of alleles and independent assortment of unlinked genes in meiosis.
10.1.U4: Crossing over produces new combinations of alleles on the chromosomes of the haploid cells.
- Draw a diagram to illustrate the formation of new allele combinations as a results of crossing over.
3.3.U7: Crossing over and random orientation promotes genetic variation.
- Explain how meiosis leads to genetic variation in gametes.
- State that the number of chromosome combinations possible due to random orientation is 2n.
3.3.U8: Fusion of gametes from different parents promotes genetic variation.
- Outline the role of fertilization as a source of genetic variation.
3.3.A1: Non-disjunction can cause Down syndrome and other chromosome abnormalities. Studies showing age of parents
influences chances of non-disjunction.
- Define non-disjunction.
- State the result of nondisjunction.
- Describe the cause and symptoms of Down syndrome.
- Explain the relationship between parental age and chances of non-disjunction.
Discovery of Meiosis: 100 Greatest Discoveries
Sexual Life Cycle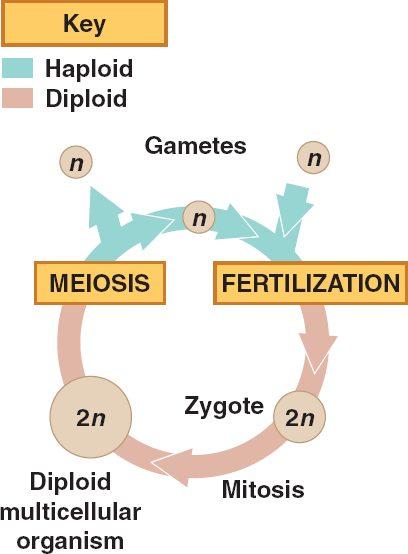
| Asexual Life Cycle |
Sources of Genetic Variation

Mitosis vs MeiosisFunction… |
|
|
Occurs in… |
|
|
Daughter Cells are Genetically… |
|
|
Crossing Over? |
|
|
Pairing of Homologs? |
|
|
Number of Divisions |
|
|
Number of Daughter Cells Produced |
|
|
Chromosome Number |
|
|
Steps |
|
|
Creates… |
|
|

- During ________________ of meiosis, homologous portions of two non-sister chromatids line up gene by gene
- In crossing over, two homologous non-sister chromatids break at corresponding points and switch fragments
- Crossing over occurs at the _________________
- Cross-over occurs randomly along entire chromosome
- Crossing over produces ____________________________________, which are combinations of alleles not present in either parent
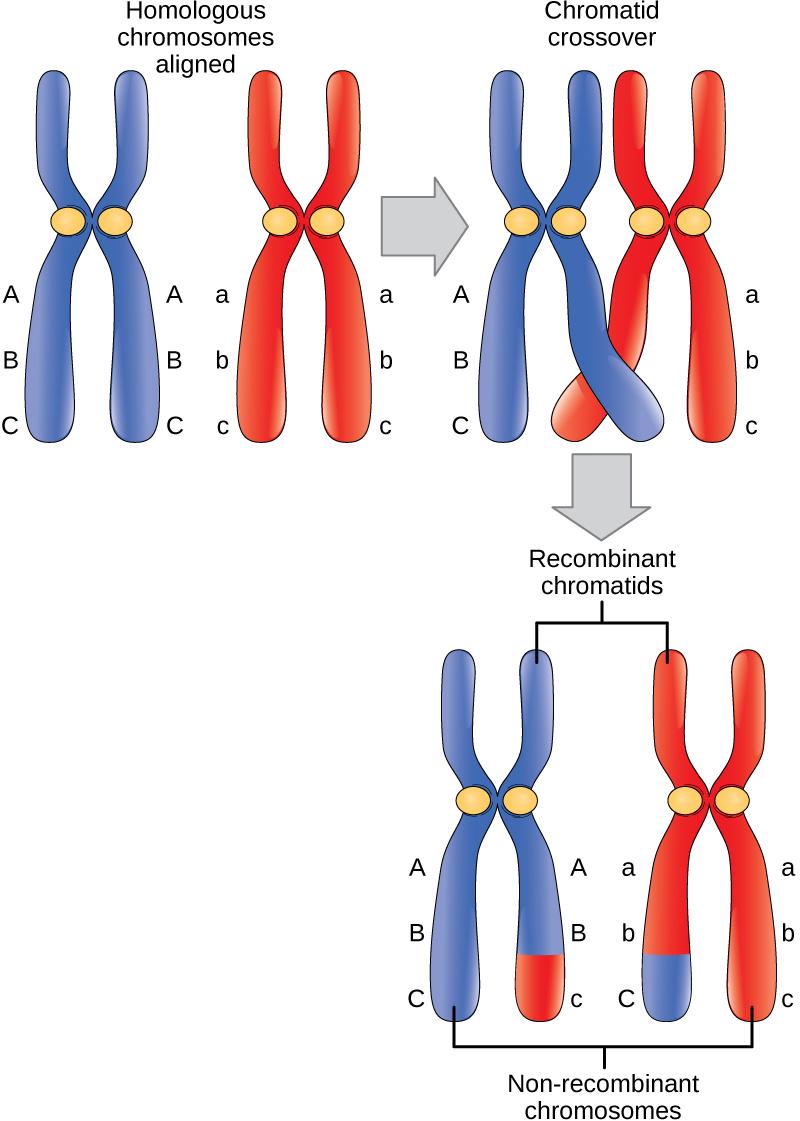

Independent Assortment of GENES
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________


Segregation of ALLELES during Meiosis

NONDISJUNCTION
Nondisjunction definition:
Nondisjunction in ANAPHASE 1 | Nondisjunction in ANAPHASE 2 |
Describe:
| Describe:
|
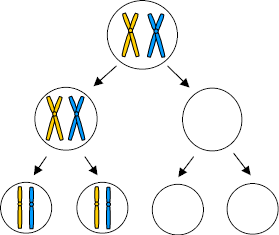
|
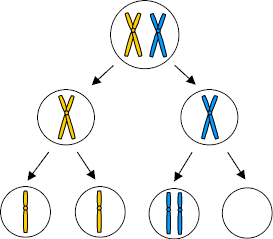
|
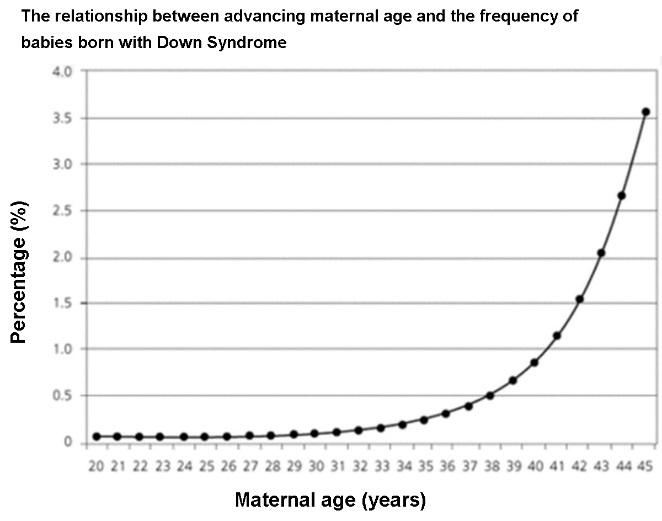
Nondisjunction and Down syndrome