UNIT _____: Climate Change Name: ________________________
Essential Idea(s):
Concentrations of gasses in the atmosphere affect climates experienced at the Earth’s surface.
IB Assessment Statements and Class Objectives
4.3.NOS: Making accurate, quantitative measurements-it is important to obtain reliable data on the concentrations of carbon dioxide and methane in the atmosphere
- Explain why accurate measurements of CO2 and methane in the atmosphere are important.
- Outline how data on concentration of atmospheric CO2 and methane are collected.
4.4.U1: Carbon dioxide and water vapor are the most significant greenhouse gasses
- State the sources of CO2 and water vapor in the atmosphere.
- Outline the mechanism by which greenhouse gasses trap heat in the atmosphere.
4.4.U2: Other gasses including methane and nitrogen oxides have less impact
- State the sources of methane and nitrogen oxide gasses in the atmosphere.
4.4.U3: The impact of a gas depends on its ability to absorb long wave radiation as well as on its concentration in the atmosphere
- State two factors that determine the warming impact of a greenhouse gas.
- State two variables that determine the concentration of a gas in the atmosphere.
- Compare the impact of atmospheric methane to CO2.
- State how long water, methane and CO2 remain in the atmosphere, on average.
4.4.U4: The warmed Earth emits longer wavelength radiation (heat)
- State that the Earth absorbs short-wave energy from the sun and re-emits longer wavelengths.
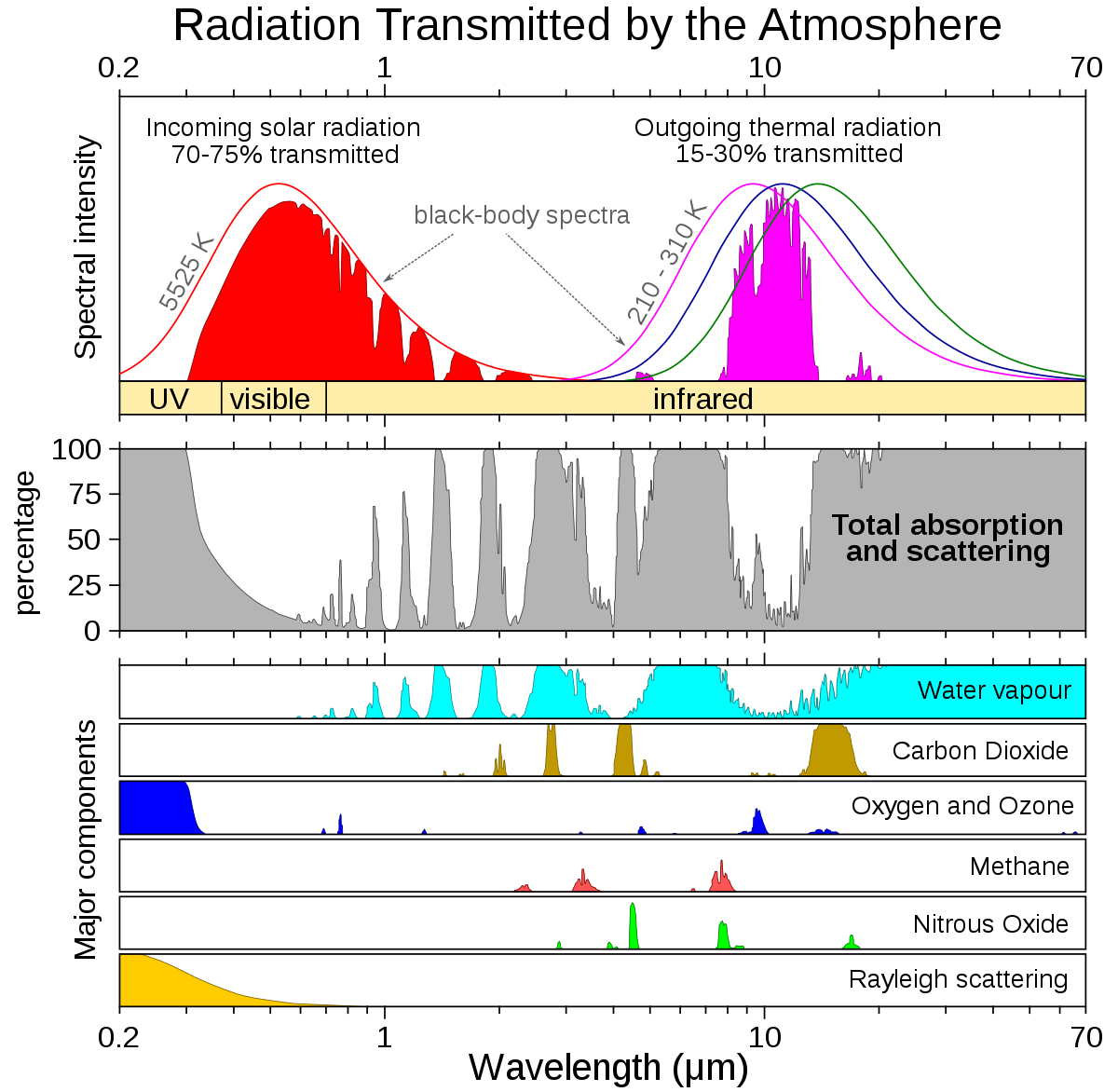
- Compare wavelengths of UV, visible and infrared radiation.
4.4.U5: Longer wave radiation is absorbed by greenhouse gasses that retain the heat in the atmosphere
- Explain the greenhouse effect, with reference to short wave radiation from the sun, long wave radiation from the Earth and the effects of ozone and greenhouse gasses.
- Explain why water vapor, CO2, methane and NO are greenhouse gasses.
4.4.U6: Global temperatures and climate patterns are influenced by concentrations of greenhouse gasses
- Explain why atmospheric CO2 concentration would logically impact global temperatures.
- Outline the effect of concentration of greenhouse gasses on climate patterns.
4.4.A1: Correlations between global temperatures and carbon dioxide concentrations on Earth
- Explain how historical temperature data has been collected.
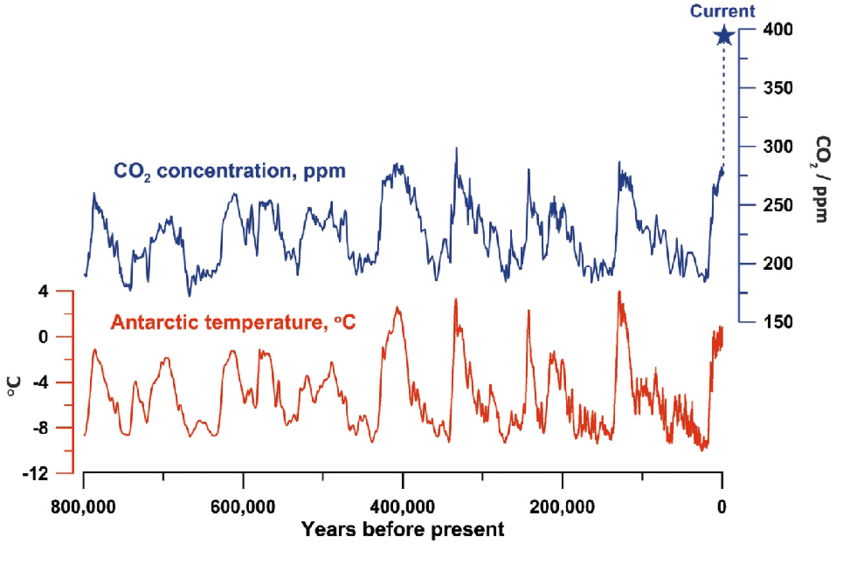
- Using ice core data, outline the correlation between atmospheric CO2 concentration and global temperatures.
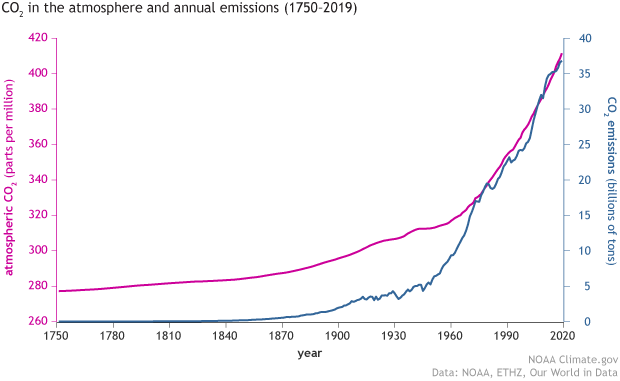
4.4.U7: There is a correlation between rising atmospheric concentrations of carbon dioxide since the start of the industrial revolution 200 years ago and average global temperatures
- State the atmospheric CO2 concentration prior to the industrial revolution.
- Outline the impact of the industrial revolution on atmospheric CO2 concentration.
- Describe the correlation between atmospheric CO2 concentrations since the industrial revolution and global temperatures.
4.4.U8: Recent increases in atmospheric carbon dioxide are largely due to increases in the combustion of fossilized organic matter.
- Explain why the industrial revolution correlates to an increase in atmospheric CO2 concentrations.
4.4.A2: Evaluating claims that human activities are not causing climate change
- Outline three reasons why there is vigorous debate around the claim that human activities are causing climate change.
4.4.A3: Threats to coral reefs from increasing concentrations of dissolved carbon dioxide
- Outline the effect of atmospheric CO2 concentration on ocean pH.
- Describe the impact of lower ocean pH on animals that make skeletons from calcium carbonate.

How are atmospheric gasses measured?
Why are atmospheric glasses measured?
Sources:
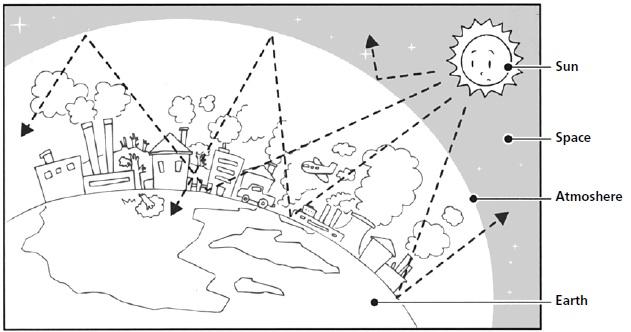
Greenhouse Effect
Definition:
- Short wave radiation from the Sun (peaks at 400 nm)
- Long wave radiation from the Earth (peaks at 10,000 nm)

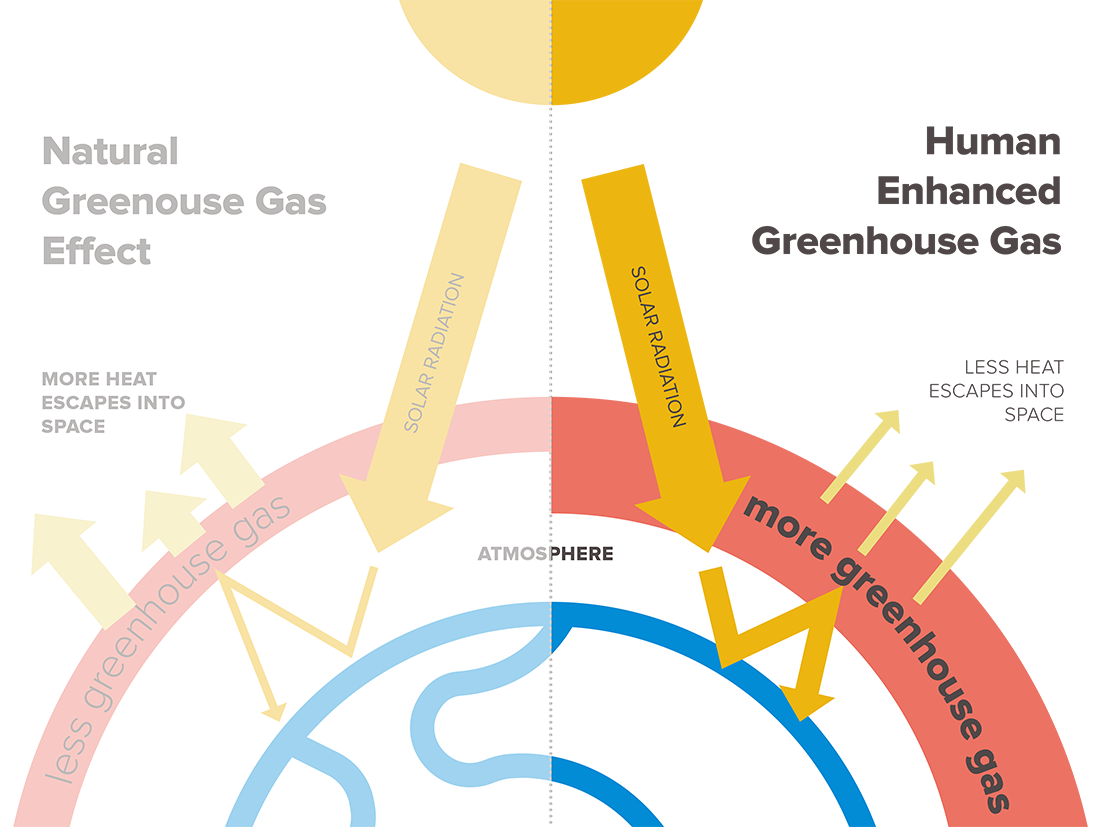
Enhanced Greenhouse Effect
Definition:
Greenhouse Gasses (1% of atmospheric gasses)
Definition:

GAS |
|
|
|
| Fluorinated Gasses |
STRUCTURE |
|
|
|
| VARIABLE |
SOURCE(S) |
|
|
|
|
|
RADIATIVE EFFICIENCY |
|
|
|
|
|
RELATIVE RATE OF RELEASE PERCENT OF US EMISSIONS (2020) |
| ❌ |
|
|
|
LIFETIME |
|
|
|
|
|
ABUNDANCE |
|
|
|
|
|
OVERALL GLOBAL WARMING POTENTIAL |
|
|
|
|
|
Correlation between Global Temperature and Carbon Dioxide Concentration
If the concentration of a greenhouse gas rises, more heat will be retained and we should expect an increase in global temperatures.
Hypothesis: If the concentration of a greenhouse gas rises, more heat will be retained and we should expect an increase in global temperatures.
- Null: there is no significant correlation between atmospheric CO2 concentration and global temperature.
- Alternative: there is a significant correlation between atmospheric CO2 concentration and global temperature.

Industrial Revolution as Major Source of Enhanced Greenhouse Effect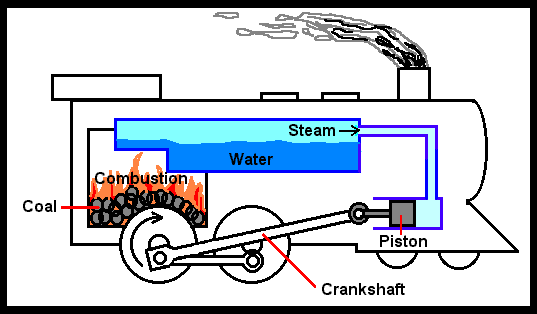
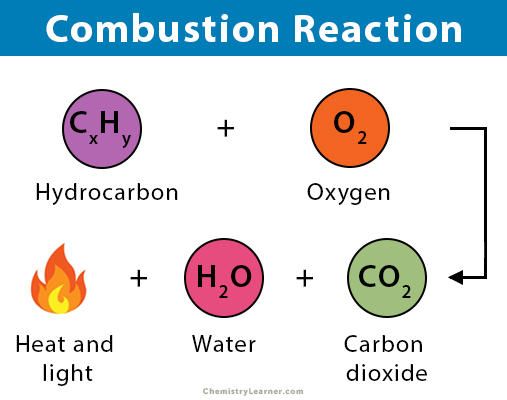

Activities that affect the amount of CO2 include:
Greenhouse Gasses and Climate Patterns:
- Increases in greenhouse gas concentrations are predicted to cause:
- ↑ global temperature average
- ↑ in frequency and intensity of heat waves and droughts in some regions
- ↑ temp 🡪 ↑ evaporation 🡪 ↑ rain in some regions (with changing patterns of distribution)
- ↑ temp 🡪 ↑ ocean temp 🡪 ↑ tropical storms and hurricanes
- Changes to ocean currents (actually leading to colder temperatures in some regions, like western Europe)
Assessing Claims that Human Activities Are Not Causing Climate Change
- Climate change has been more politically debated than almost any other area of science. Why?
- Why 50-50 debates are inherently misleading:
Ocean Acidification
Definition:
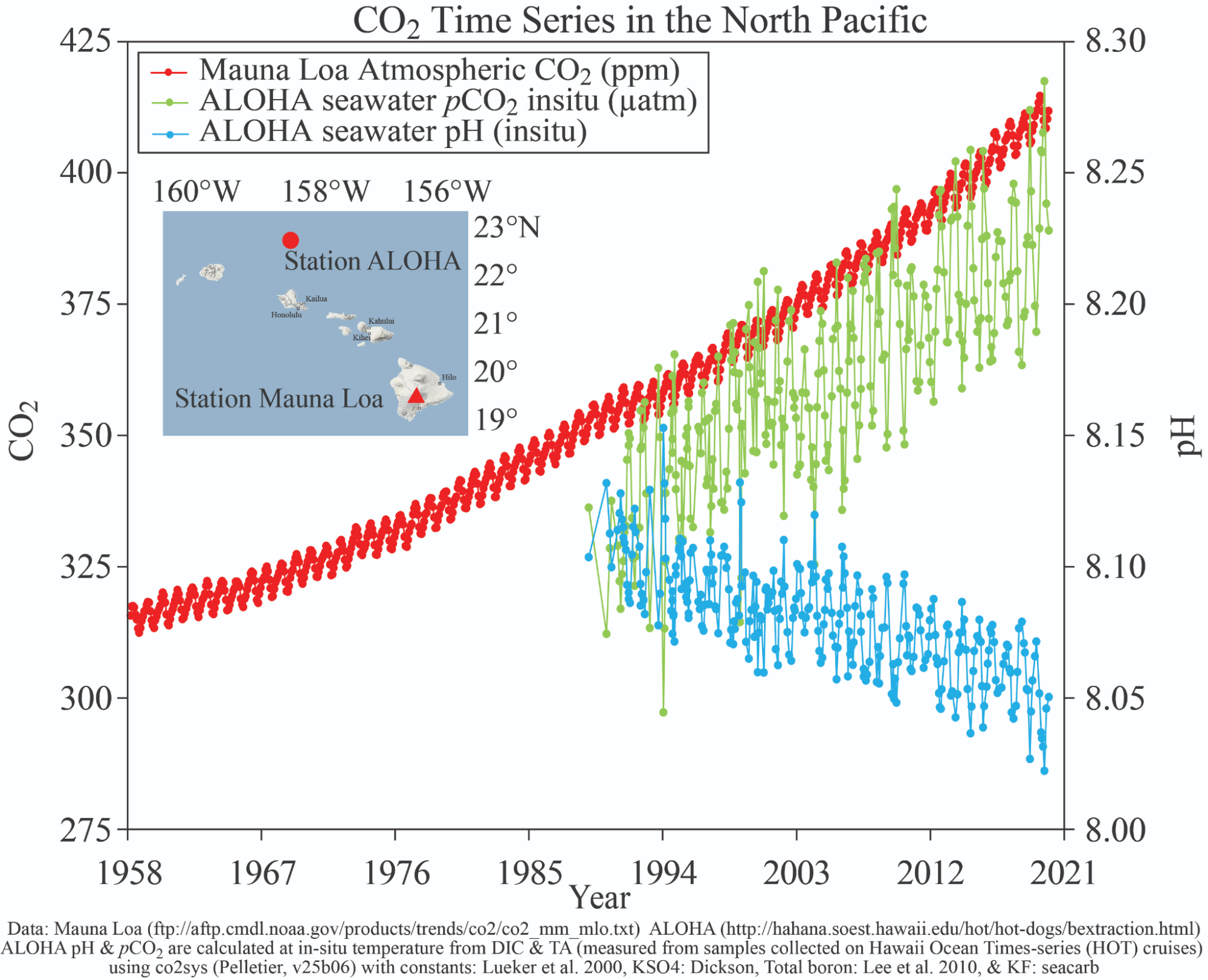
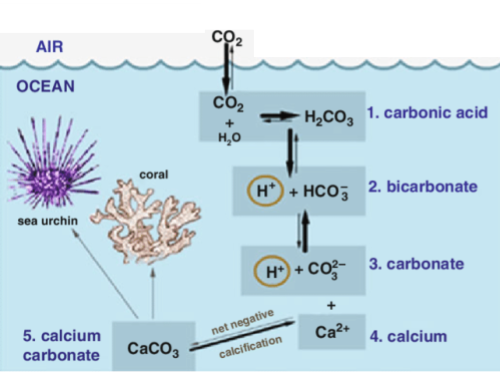
Acidification affects marine life:
