Unit ____: Adaptations to Niches over Time Name: _____________________________
THEMES: | Commonality with Diversity | Form and Function | Interaction and Interdependence | Feedback for Regulation | Nature of Science | |
LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION: | Molecules | Cells | Organisms | Ecosystems | ||
Every organism has a niche; the organism’s habitat, its tolerance limits and its function within that habit (C.1).
Species have adapted through natural selection to fill available niches (5.2.U3).
Evolution of homologous structures by divergent evolution explains similarities in structure when there are differences in function (5.1.U4).
Examples of homologous structures include the pentadactyl limb and the modification of leaves and flowers (5.1.A1, 5.1.NOS).
The fossil record provides evidence of divergent evolution (5.1.U2).
When a change in the environment opens new environmental niches, organisms diversify rapidly from an ancestral species into a multitude of new forms (5.1.U4)
Gradualism and punctuated equilibrium are two ways in which the evolution of a species can occur. (10.3.U4 and 10.3.U5)
Analogous structures evolve by convergent evolution to fulfill the same function (5.4.U4).
Ecological Niche
temperature, precipitation, solar radiation, terrain
competition, predation, mutualism
nocturnal, diurnal, phenology
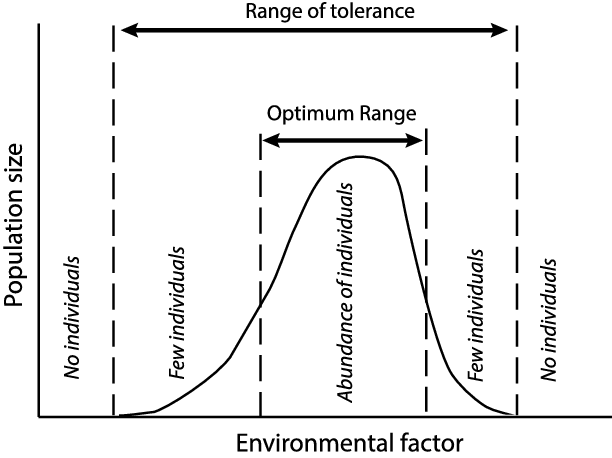
Range of Tolerance
For any environmental factor there will be a range which a particular species can tolerate.
Niches are restricted by the competition between species for resources.
Species have adapted through natural selection to fill available niches
Adaptations
Structural Adaptations | Physiological Adaptations | Behavioral Adaptations |
Homologous Structures
Define:
Homologous structures are the result of divergent evolution.
Pentadactyl Limb as Homologous Structure
In tetrapods, the basic pentadactyl limb has been adapted to serve specialized locomotory functions.
Such homologies indicate divergent evolution, as the basic limb plan has been adapted to meet the needs of different niches.
Leaf as Homologous Structure
In some plants the leaves show different functions and shapes from the 'normal' leaves we think about.
However, these structures share common ancestry with typical leaves, and as such are homologous!
Flower as Homologous Structure
The general flower structure pattern is homologous, meaning it is a similarity due to shared ancestry of all angiospermatophyta. A typical flower has four major structures:
As flowering plants diversified, different lineages evolved to use these basic parts in different ways.
Fossils
The fossil record is a substantial, but incomplete, record of evolutionary history:
Adaptive Radiation
Define:
EXAMPLES:
Example | What caused the niches to be available for new species? | What was the ancestral species? | How many species were formed from the ancestral species? | How many years did it take for the adaptive radiation to occur? |
Mammals after dinosaur extinction | ||||
Finches on Galapagos Islands | ||||
Ant Nest Beetles on Madagascar | ||||
Silversword on the Hawaiian Islands | ||||
Anoles on Caribbean Islands |
Pace of Evolution
Gradualism | Punctuated Equilibrium |
|
|
Analogous Structures
Define:
Analogous structures are the result of convergent evolution.
EXAMPLES:
illustrate two examples