Unit ____: Natural Selection Name: _____________________________
THEMES: | Commonality with Diversity | Form and Function | Interaction and Interdependence | Feedback for Regulation | Nature of Science | |
LEVELS OF ORGANIZATION: | Molecules | Cells | Organisms | Ecosystems | ||
Natural selection increases the frequency of characteristics that make individuals better adapted. This leads to changes within the species (5.1.U1 and 5.2.U7).
Species tend to produce more offspring than the environment can support (5.2.U4).
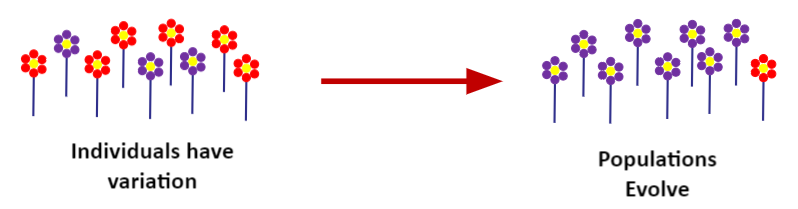
Natural Selection can only occur if there is variation among members of the same species (5.2.U1, 5.2.U2 and 10.2.U3).
Selective pressures influence the survival and reproduction of individuals in a population.
Individuals that are better adapted tend to survive and reproduce, passing on the favorable adaptation to their offspring while those who are less well-adapted tend to produce fewer or no offspring (5.2.U3, 5.2.U5 and 5.2.U6).
Evolution is the change in the heritable characteristics of a population over successive generations.
Natural selection can change the frequency of individuals with particular traits, depending which phenotype is more favorable within a particular environment (10.3.A1).
Evolution
Definition:
Natural Selection
POTENTIAL OVERPRODUCTION OF OFFSPRING
Exponential Population Growth: | Logistic Population Growth: |
When resources are unlimited, populations exhibit exponential growth, resulting in a J-shaped curve. | When resources are limited, populations exhibit logistic growth. Population expansion decreases as resources become scarce. It levels off when the carrying capacity of the environment is reached, resulting in an S-shaped curve. |
No = 2 r = 1.6 Population after:
| No = 2 r = 1.6 K = 1000 Population after:
|
Genetic Variation in the Population
Discrete and Continuous Variation
Discrete Variation | Continuous Variation | |
Description | ||
Cause | ||
Graph | ||
Examples |
Sources of Genetic Variation: Mutation
Description | Result | Sketch | ||
Sources of Genetic Variation: Meiosis
Description | Result | Sketch | ||
Crossing Over | ||||
Independent Assortment | ||||
Segregation of Alleles | ||||
Sources of Genetic Variation: Sexual Reproduction
Description | Result | Sketch | ||
Random Mating between Organisms | ||||
Random Fertilization | ||||
Sources of Genetic Variation: Gene Flow
Description | Result | Sketch | ||
Define:
Examples:
✔ Adaptation ✔ | ✖ Response ✖ |
Adaptations
Example | Selective Pressure | Adaptation |
INSECTS MIMICKING LEAVES | ||
CREOSOTE BUSH | ||
ECHOLOCATION IN BATS | ||
LACTASE PERSISTENCE IN HUMANS | ||
ICEFISH BLOOD | ||
STICKLEBACK SPINES | ||
ROCK POCKET MICE FUR COLOR | ||
ELEPHANT COMMUNICATION |
How does the strength of selection affect the rate at which populations change?
Modes of Natural Selection
Stabilizing Selection
Initial Population | Population After Selection | Description | Example(s) |
Directional Selection
Initial Population | Population After Selection | Description | Example(s) |
Disruptive Selection
Initial Population | Population After Selection | Description | Example(s) |